Set Git Bash as the Default Shell for SSH on Windows 10
To make Git Bash the default shell for SSH connections on a Windows 10 machine, follow these steps:
Step 1: Enable SSH Server on Windows 10
Open PowerShell as an Administrator.
Install OpenSSH Server:
Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name OpenSSH.Server~~~~0.0.1.0
Enable and Start the SSH Server:
Set-Service -Name sshd -StartupType 'Automatic'
Start-Service -Name sshd
Step 2: Install Git via Chocolatey
Install Chocolatey:
Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Scope Process -Force; [System.Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [System.Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol -bor 3072; iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('https://community.chocolatey.org/install.ps1'))
Install Git:
choco install git -y
Step 3: Set Git Bash as the Default Shell for SSH
Run the following command to set Git Bash as the default shell for the SSH service:
This command updates the registry to make Git Bash the default shell for SSH connections.
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\OpenSSH" -Name "DefaultShell" -Value "C:\Program Files\Git\bin\bash.exe" -PropertyType String -Force
Step 4: Test SSH Login
On another machine, open a terminal and try logging in via SSH:
Upon successful login, you should be automatically switched to Git Bash.
ssh <username>@<your-windows-machine>
e.g. ssh [email protected]
Key-based authentication in OpenSSH for Windows
Move to the .ssh Directory(Client):
cd .sshChanges the current directory to
.ssh, which typically stores SSH keys.Generate a New SSH Key Pair:
ssh-keygen|– id_rsa
|– id_rsa.pub
Copy the Public Key to the Remote Server:
as name:
administrators_authorized_keys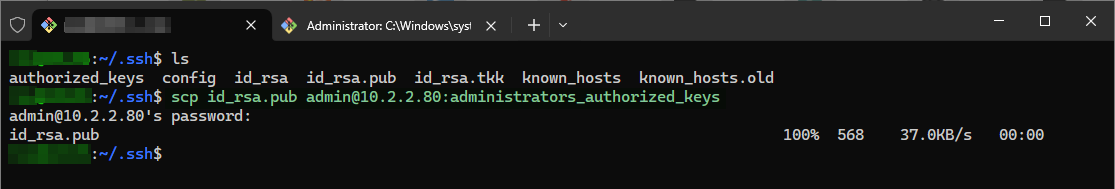
scp id_rsa.pub [email protected]:administrators_authorized_keysUses
scp(secure copy) to transfer the public key fileid_rsa.pubto the remote server at IP10.2.2.80. The file will be saved asadministrators_authorized_keyson the remote server under theadminuser’s home directory.SSH into the Remote Server(Server):
ssh USER@RemoteIPSSH connection to the remote server specified by
RemoteIPusing theUSERaccount.adminas username and10.2.2.80with the IP address of the remote server.Move the Key File to the SSH Configuration Directory:
move administrators_authorized_keys %ProgramData%\sshMoves the
administrators_authorized_keysfile to the%ProgramData%\sshdirectory, which is where Windows stores SSH configuration files.Move to the SSH Directory:
cd %ProgramData%\sshChanges the current directory to
%ProgramData%\ssh.Set Permissions on the Authorized Keys File:
bash
icacls administrators_authorized_keys /inheritance:r /grant "Administrators:F" /grant "SYSTEM:F"Modifies the permissions of the
administrators_authorized_keysfile. It removes inherited permissions and grants full control to theAdministratorsgroup and theSYSTEMaccount.Use the SSH keys to connect to a remote system without using passwords(Test).
ssh -tq [email protected] "shutdown -s -f -t 0
One-time to Deploy a SSH Public Key on Windows 10
Run “PowerShell” as administrator
Type [A] to grant unrestricted access.
This script consolidates all steps.🚀
- Check if OpenSSH Server is installed
- Check if SSH service is running
- Fetch the SSH public key from my github
- Display network configuration details
Set-ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted
$LocalFilePath = "C:\Temp\ssh-key-on-win.ps1"
if (!(Test-Path "C:\Temp")) {
New-Item -ItemType Directory -Path "C:\Temp"
}
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "https://kingtam.eu.org/scripts/ssh-key-on-win.ps1" -OutFile $LocalFilePath
PowerShell -File $LocalFilePath
Connects to a remote server without a password, immediately shuts down the remote server, force-closing all applications.
