Introduction:
This is a basic network configuration guide for Cisco routers, and all exercises are based on a simulator (EVE-NG).
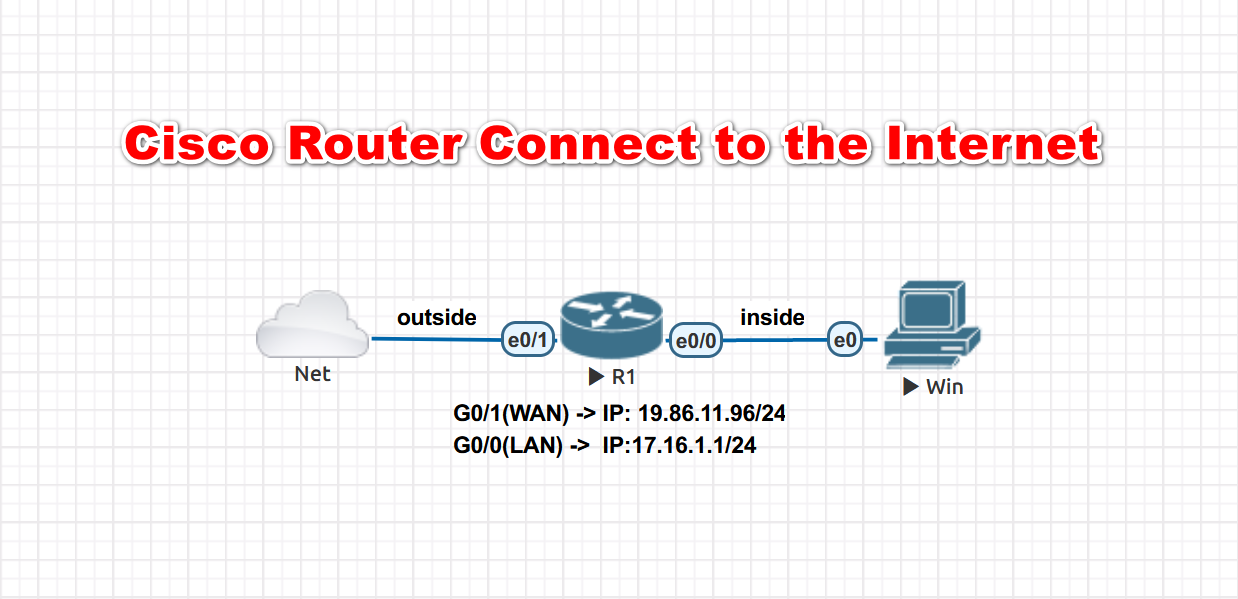
Enable and Configure Port IP Addresses
In this example,
interface Ethernet0/0is theLANport, andinterface Ethernet0/1is theWANport.
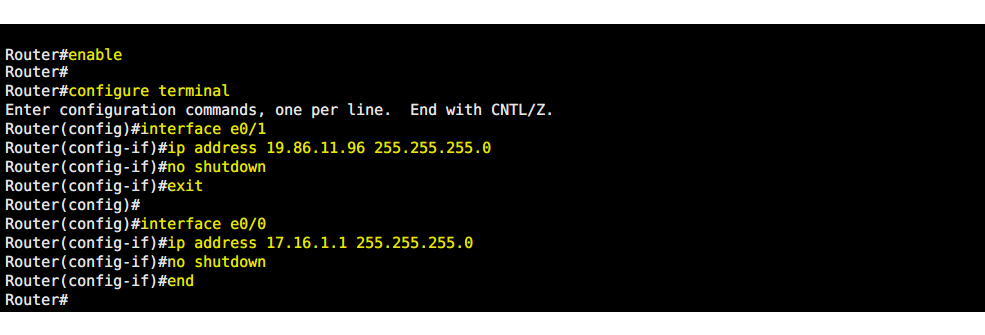
Router#enable
Router#
Router#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#
Router(config)#interface e0/1
Router(config-if)#ip address 19.86.11.96 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#no shutdown
Router(config-if)#exit
Router(config)#
Router(config)#interface e0/0
Router(config-if)#ip address 17.16.1.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#no shutdown
Router(config-if)#end
Check IP Addresses for Port
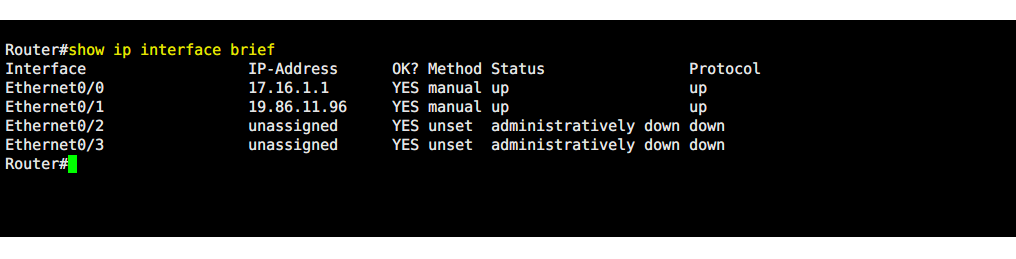
Router#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol Ethernet0/0 17.16.1.1 YES manual up up Ethernet0/1 19.86.11.96 YES manual up up
Configure DHCP Server
Each device that connects to the Internet needs a unique IP address. DHCP enables network administrators to monitor and allocate IP addresses from a central node. When a computer is moved to another location on the network, it can automatically receive a new IP address. From Wiki
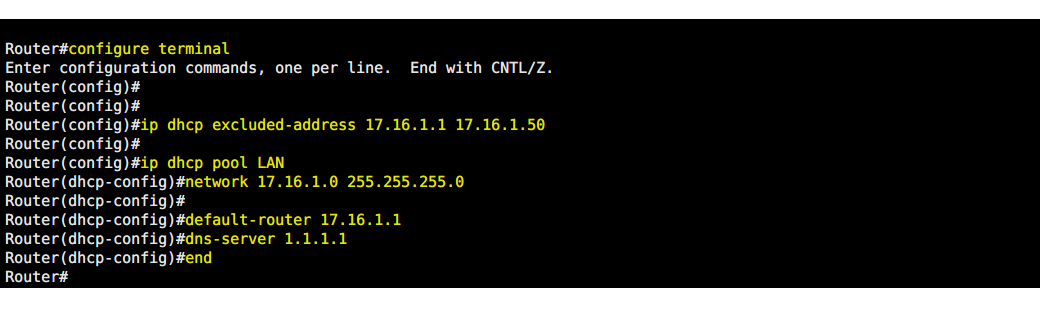
Router#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#
Router(config)#ip dhcp excl
Router(config)#ip dhcp excluded-address 17.16.1.1 17.16.1.50
Router(config)#
Router(config)#ip dhcp pool LAN
Router(dhcp-config)#network 17.16.1.0 255.255.255.0
Router(dhcp-config)#default-router 17.16.1.1
Router(dhcp-config)#dns-server 1.1.1.1
Router(dhcp-config)#end
Test with Client Computers:
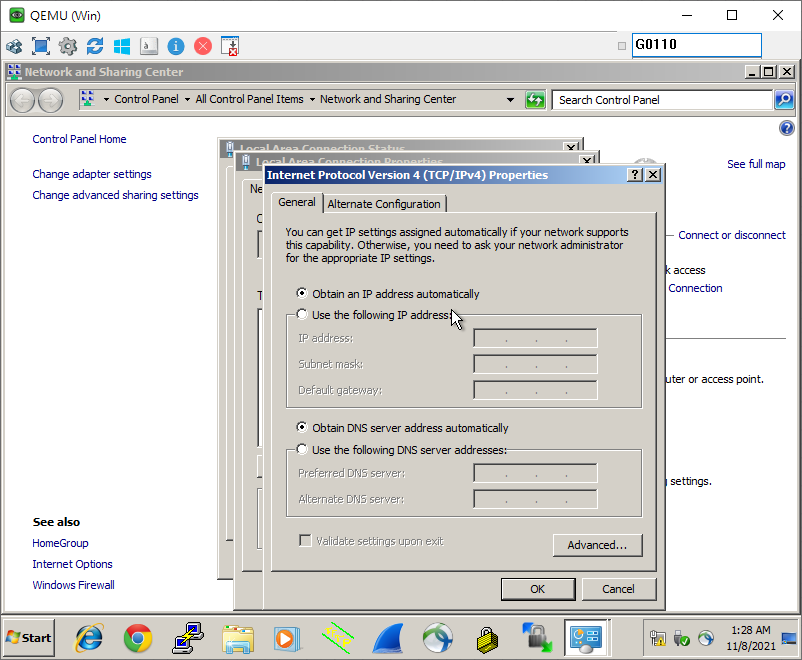
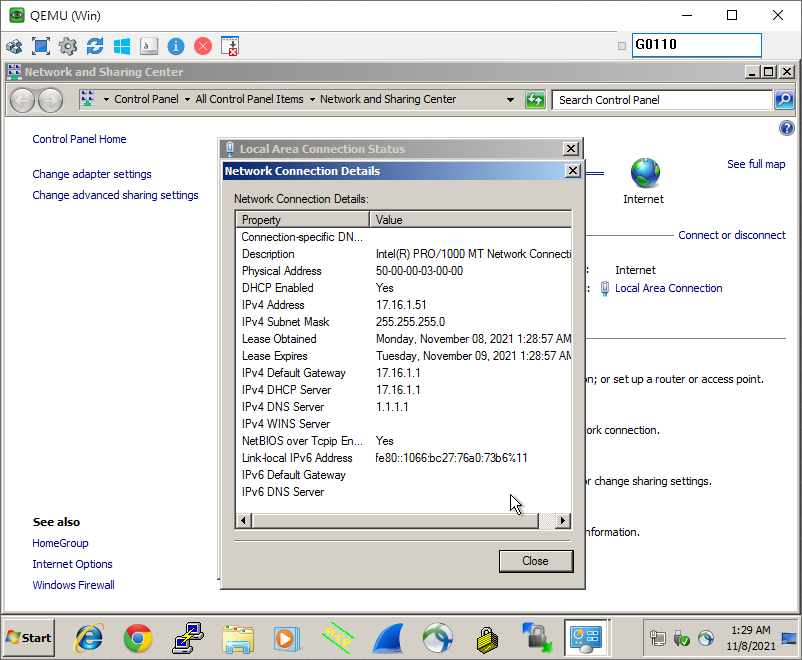
NAT(Network Address Translation)
Simply put, all devices on the internal network share one external IP address. This is a technology that rewrites the source IP address or destination IP address of IP packets when they pass through a router or firewall. From: Wiki
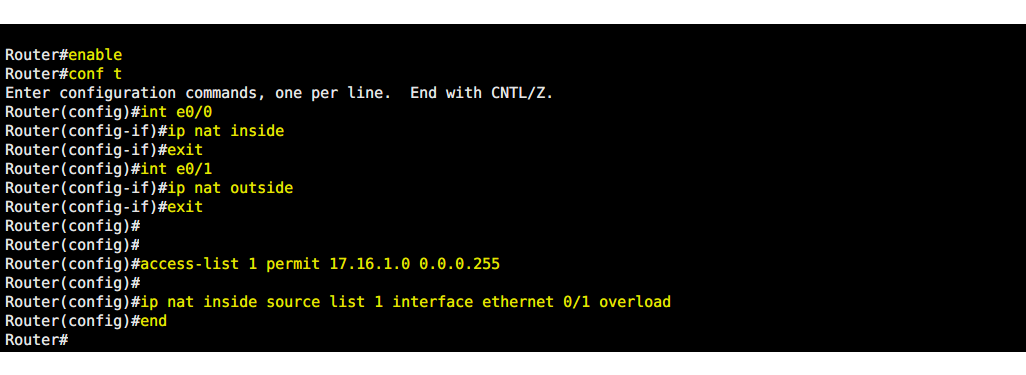
Router#enable
Router#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#int e0/0
Router(config-if)#ip nat inside
Router(config-if)#exit
Router(config)#int e0/1
Router(config-if)#ip nat outside
Router(config-if)#exit
Router(config)#
Router(config)#
Router(config)#access-list 1 permit 17.16.1.0 0.0.0.255
Router(config)#
Router(config)#ip nat inside source list 1 interface ethernet 0/1 overload
Router(config)#end
Route
A router is a networking device that forwards data packets between computer networks. Routers perform the traffic directing functions on the Internet. From Wiki
Default Route Configuration
A default route is a route that is used by a router when no other known route exists for a given IP address destination.
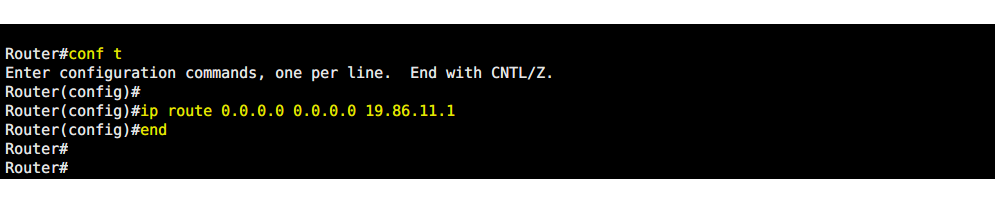
Router#enable
Router#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#
Router(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 19.86.11.1
Router(config)#end
Check Routes:
Router#show ip route
Internet Connection Test:
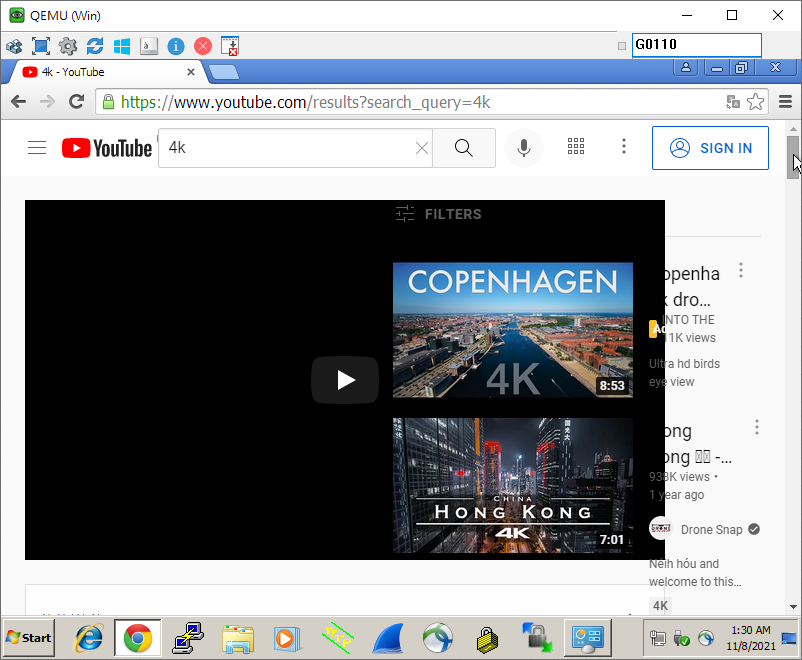
Port-Forwarding
Port forwarding is a technique that is used to allow external devices access to a specific computer or service within a private local-area network (LAN). It is done by mapping a public IP address to a private IP address and specific port number. From Wiki
Configuration
In this example, we use port 3389 of Remote Desktop to access the computer (Windows7) with IP address 17.16.1.51 in the internal network.
Router#enable
Router#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#
Router(config)#ip nat inside source static tcp 17.16.1.51 3389 19.86.11.96 3389
Router(config)#exit
Check with Test
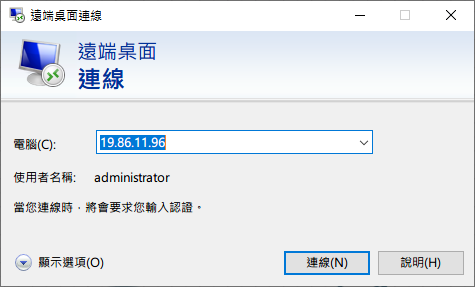
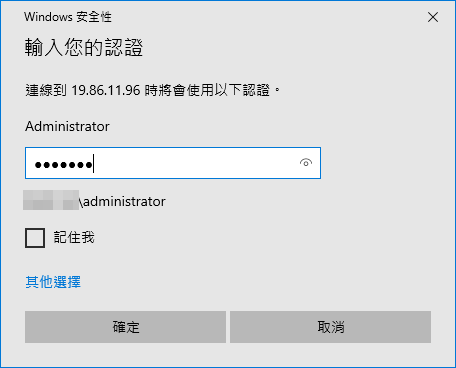
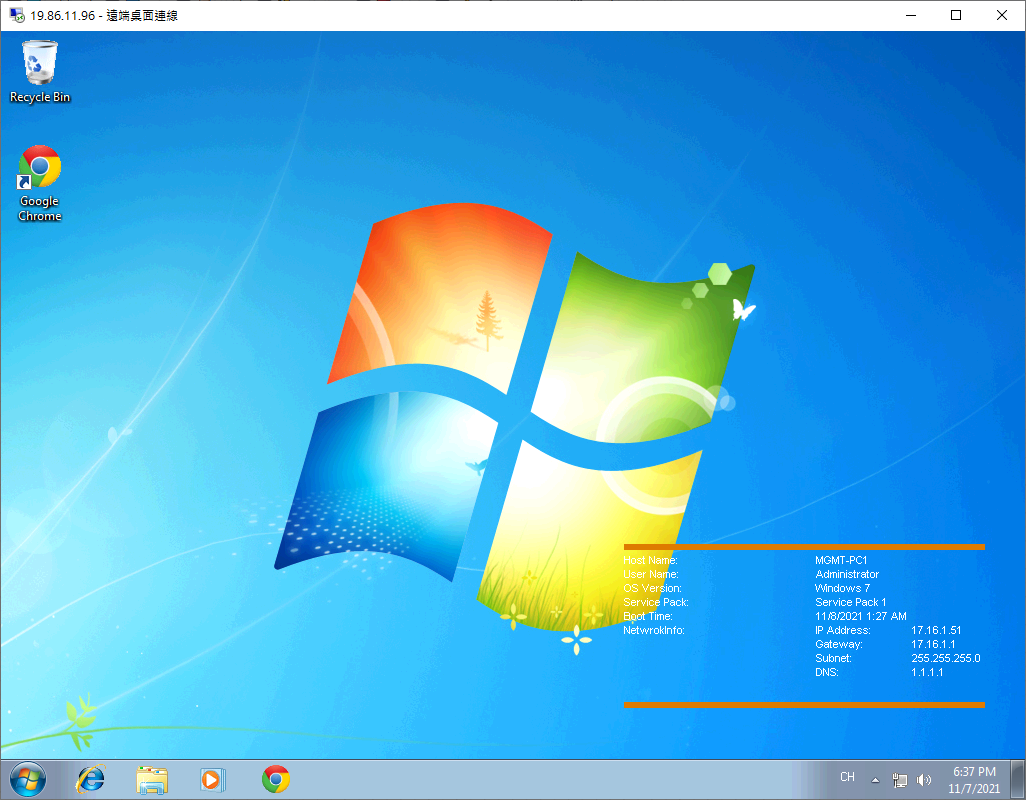
Finally, remember to “save” all settings
Router#write memory
Building configuration...
[OK]
Conclusion:
Compared with home routers, setting up Cisco routers is more cumbersome because home routers already have default
WANandLAN (bridge)settings, while Cisco routers are based on commercial use, and each configuration step requires a deeper understanding of the network.
